The tap is a tool for processing various medium and small size internal threads. It has a simple structure and is easy to use. It can be operated manually or on a machine tool. It is widely used in production. What are the relevant knowledge of tapping? The summary of this article is very comprehensive.
1. What is tapping
Tapping is to use a tap to cut the internal thread inside the hole of the workpiece.
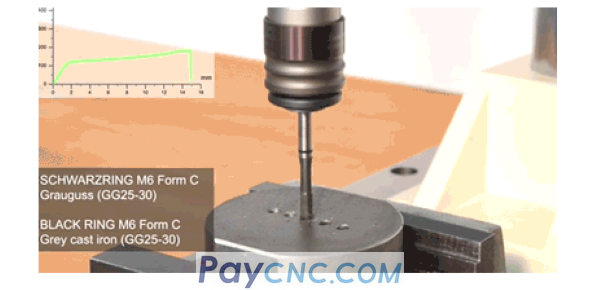
(1) The factors that determine the performance of the tap include:
Workpiece material
Cutting speed
Cutting edge material
Knife handle
Taper type
Hole size
Tapping tool holder
Cutting fluid
Hole depth
(2) Pitch: the axial distance between two adjacent teeth on the thread on the corresponding two points on the pitch line.
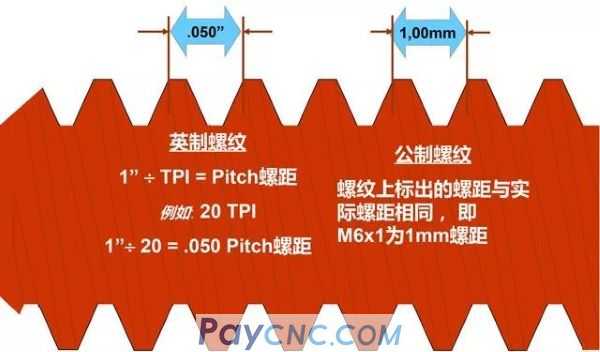
(3) Lead: the axial distance between the corresponding points of two adjacent teeth on the same spiral line. It is represented by the code S.

(4) Nominal diameter of thread: Except for pipe thread whose inner diameter (in inches) is the nominal diameter of the pipe, the nominal diameter of other threads is the major diameter of the thread (metric unit).
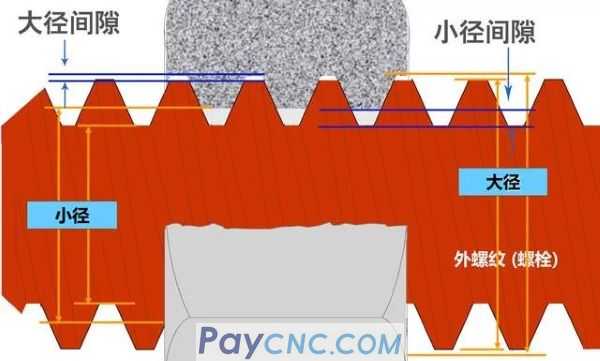
(5) Thread pitch diameter: The pitch diameter is the most important because it controls the fit and strength of all thread assemblies. The pitch diameter is on the pitch line, and the width of the tooth at this position is consistent with the width of the adjacent tooth groove.

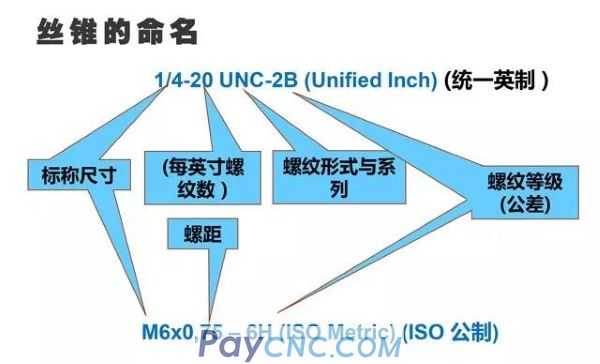
2. The naming of threads
Inch thread: Inch thread is the size of the thread marked in inch, which was developed by the United States, Britain and Canada according to a unified system.
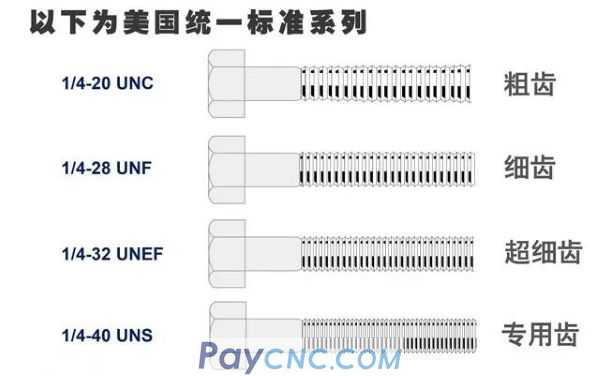
Metric thread: Developed according to the ISO (International Organization for Standardization) system, it is the global standard for metric threads.
3. Design high-performance tapping processing
(1) Perfect application
The factors that need to be considered in the tapping process are: workpiece design, tap design, and application. The goal is to reduce the cutting force while maximizing the strength of the tap.
(2) Balance various options: all aspects of the application must be considered

(3) Key points of tap design
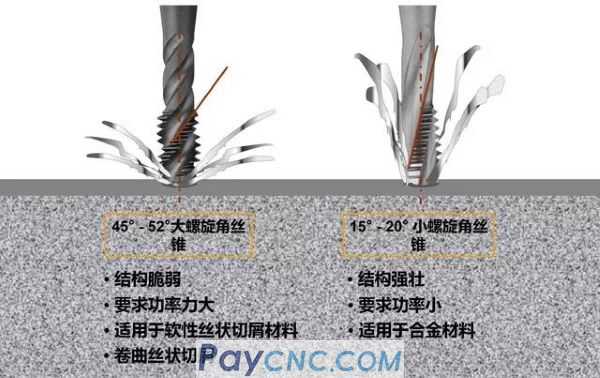
1) For soft viscous materials that form long chips
Simple tap structure
Large front angle and hook angle
Large clearance angle and avoidance
Free cutting
Easy to chip
The overall tap is weak
Large chip space
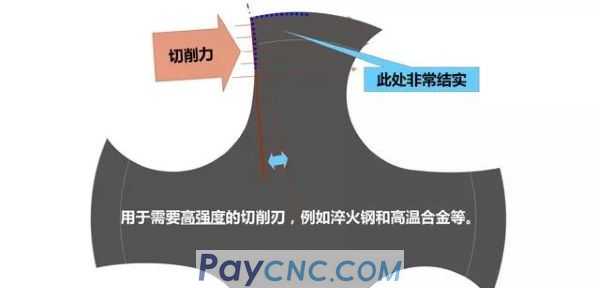
2) For hard materials
The tap has a heavy-duty structure
Small front angle and hook angle
Shovel back and small rear angle
Higher cutting pressure
The design of the cutting edge is sturdy to reduce chipping
Large cross section
Limited chip space
(4) Factors to be considered for tap design: tap groove type, tool material, surface strengthening treatment. These design features must be balanced to provide proper cutting, chip control, lubrication and torsional strength.
*Note: What action must the tap do in tapping, but other tools do not need it?
You must stop in the middle of the cutting and reverse the hole, while the cutting remains in the groove. This brings one of the biggest challenges to tapping and tap design in metal processing.
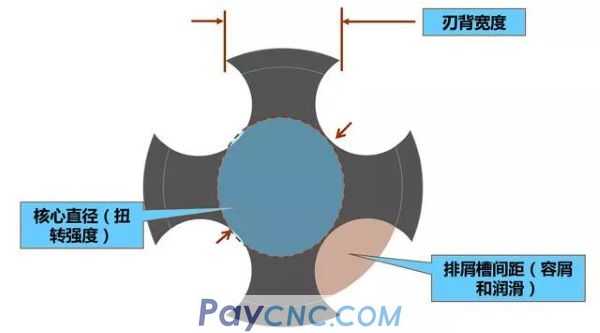
4. The shape of the tap
(1) Type of tap cutting surface
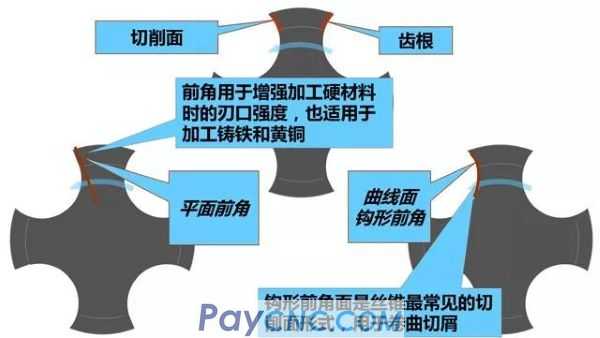
① Correctly select the positive hook type tap

②The correct selection of small taps or negative hook angle taps
(2) Tap cutting cone
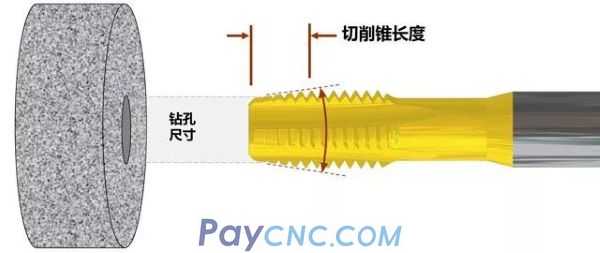 
Every time a cutting bevel tooth is added, the service life of the tap will be extended exponentially. Tests have shown that for every half of the cutting tooth thread, the tool life will double. Unlike other tools, the chip load of a tap can only change with the number of flutes and the length of the cutting cone.
(3) Inverted taper: similar to all other tools, the tap is also slightly inverted.

(4) Threaded shovel back
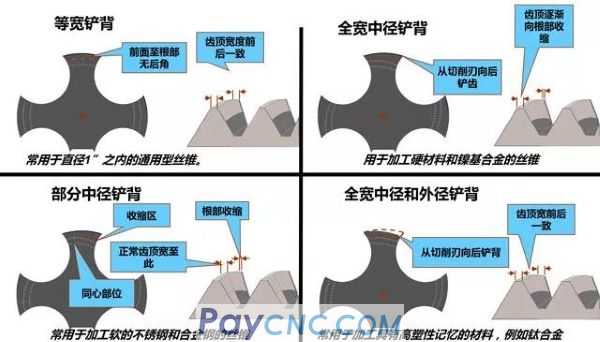
The advantages of threaded shovel back are:
Cutting is brisk, less heat accumulation
Twisted on the tap, less bonded material (sticky chips, less built-up edge)
Higher tapping speed can be used
Compensate for plastic deformation of workpiece material
The disadvantages of threaded shovel back are:
The cutting edge becomes brittle and easy to chip
Insufficient rigidity of the spindle and clamping (including floating tool holder) will cause the thread to be out of tolerance
Very fine chips may be embedded and chip the cutting edge during reversal
(5) Tap tolerance
Each tap has a dedicated pitch diameter.
Taps with H or D tolerance (mainly American taps)
H/D tolerance indicates the thread size of the tap.
The letter indicates whether the size of the tap is larger or higher than the basic pitch diameter ("H"=English system, "D"=metric system) or lower than the basic pitch diameter ("L"=English system, "DU"=metric system).
The actual tap size number is related to the basic pitch diameter, such as: H2, D3, L1, or DU2. Each tap has its own pitch diameter size!
Taps are often marked with thread grade
Universal HP Tap Series
Indicate that the tap is the correct size that meets the matching level of the component
Grade 3B taps are suitable for Grade 2B components
The grades of taps marked with "X" indicate larger tolerances and are used for precision taps, electroplated or heat-treated parts, or for materials that are close to (elastic memory).
Electroplated tapped threads
For internal threads, you must choose a tap with a larger tolerance level
A larger pitch diameter will make the thread size slightly larger
The increase after plating will make the thread size return to the specified value
5. Cutting treatment of tap
(1) Hole type and chip treatment

(2) Extrusion cutting, spiral chip flute tap
Most suitable for blind hole and deep hole machining
Recommended for materials that produce sticky chips
Ideal for interrupted cutting
The core of the spiral flute tap is very thin, which is the weakest part of the tap design. Therefore, the speed should be 30% ~ 40% lower than that of the straight chip flute tap to avoid breakage.
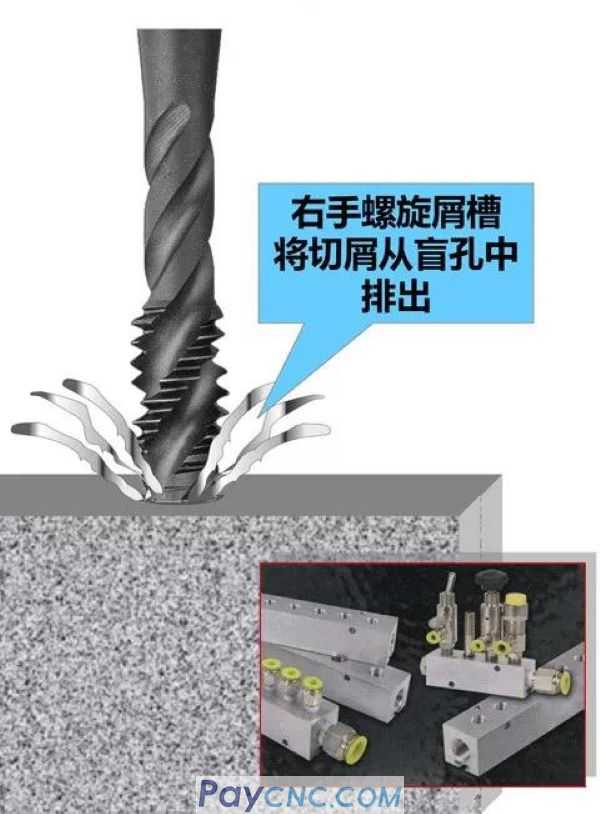
(3) Pull out and cut
(4) Straight chip flute tap
The strongest tap
Recommended for materials that break easily, such as brass and cast iron or hardened steel
Usually requires coolant or gas to flush the chips in the chip flute
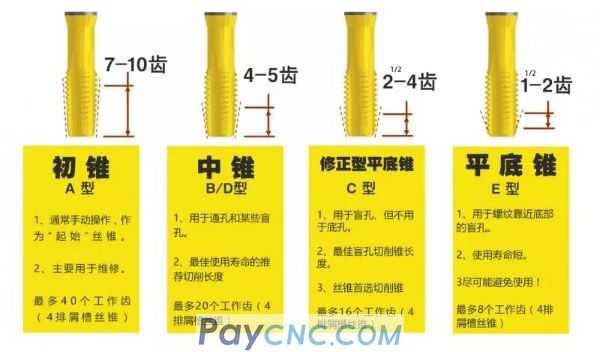
Can have a variety of cutting cones
– Taper (Form A) "A"-Initial taper
– Plug (Forms B & D) "B/D" – Middle cone
– (Form C) "C"-Semi-flat bottom or modified flat bottom
– (Form E) "E" – flat bottom

(5) Extrusion tap: Its processing feature is that no chips are generated in either through holes or blind holes.

(6) Comparison of cutting taps and extrusion taps
(7) Influence of bottom hole size on extruded thread
6. Coating of tap
(1) Advantages of coating
①Surface treatment
Improve the appearance of HSS taps
Will not change the size of the tap
②The tap life is improved
High wear resistance
Reduce friction and power consumption
Reduce chipping and breaking
Surface hardness increased slightly
③Improve the surface quality and dimensional accuracy of screw holes
Keep the cutting edge sharp
Has a lubricating effect
Reduce load and scratches
Least buildup
(2) What is built-up tumor?
The material of the workpiece is welded or seized to the accumulation on the cutting edge.
(3) Traditional surface treatment
(4) Thin film coating
7. Tips for successful tapping
(1) Determine the thread percentage
The drill hole size determines the percentage of the bottom diameter of the thread to the height of the thread. The larger the diameter of the drill you use, the smaller the ratio of the height of the thread!
(2) Selection of bottom hole size
Generally, 65% to 70% of the thread height is preferred!
The 83% height thread is only 2% stronger than the 65% height thread, but the tapping torque is more than twice that!
(3) Common problems
① Reasons for top cut
Manual tapping
-Manual feed is not coordinated, feed is too fast or too slow
Machine tapping
– Improper programming of asynchronous tapping cycles
Screw machine
-Backlash caused by the wear of the screw or the loosening of the screw adjusting nut
Cam feed machine
-The cam profile is incorrect or worn
Machine tools using pneumatic or hydraulic
-Uncontrollable, the pressure is too high or too low
Gear feed machine
-Backlash caused by improper gear adjustment or wear
②Solve the problem of cut top
For the most precise threads, the feed should be synchronized with the spindle speed! The feed and spindle rotation must match the thread pitch.
(6) Advantages of CNC machine tool synchronous tapping
Thread depth control
Same size from hole to hole
Eliminate topping
Re-attack if necessary
(7) Choice of tool holder
Used for asynchronous tapping
– CNC machine tools with fixed tapping cycles with drilling feed
-Cam, gear, pneumatic, or hydraulic feed mechanism
For synchronous tapping
– When encountering oversized/undersized threads
(8) Tool holder maintenance
Proper tool holder maintenance can ensure high-quality threads and the service life of the taps.
There should be no chips and debris in the internal mechanism
Regular lubrication ensures flexible movement of parts and prevents rust
Always test tool holders, especially when using water-soluble coolant
8. Troubleshooting
(1) The thread is too large
Tapping CNC setting
When tapping on CNC machine tools without rigid tapping cycles:
The programmed feed rate is 95-98% of the reverse stroke of the tap
Use only extended handles or telescopic handles with compression lock
When tapping on a CNC machine with rigid tapping cycle:
The tap lead is programmed to feed 100%
Use integral tool holder or synchronous tool holder
If the top cut makes the end of the thread gauge pass:
Reprogram, follow the "non-rigid" procedure
Consider using quick-change couplings. Can have a minimum "float"
(2) Chip entanglement
Change taper type
→Straight groove
→Small helix angle
Shorten the cutting cone
Change the shape of the front corner
Increase the number of slots
Change speed
Smaller hook
For rigid tapping, increase the pecking cycle
Consider extrusion tap
(3) Lubrication selection
For tapping, the purpose of lubrication is to reduce friction. Therefore, generally, lubricant is used for tapping instead of coolant; if it is coolant, EP (extra high pressure) or HP (high pressure) additives should be added.
The tap has a fixed large amount of feed, which is controlled by the tap pitch, and the drilling feed can be adjusted to the controlled load.
(4) Coolant application
9. The basis of tap selection
Before choosing a tap, we need to understand:
Type of hole, through hole, blind hole or deep hole
Minimum drilling depth
Minimum required thread depth
Whether to consider using extrusion taps
Workpiece material for tapping
|
 |
| Products Catalogue | Home | About Us | Retrofit | Download | News | Tech Support | Contact Us | |
|
|
|
